 This article will discuss the input parameters in the Distributed Loads table and gives some worked examples on how to input distributed loads into ClearCalcs for structural design applications.
This article will discuss the input parameters in the Distributed Loads table and gives some worked examples on how to input distributed loads into ClearCalcs for structural design applications.
Input Parameters
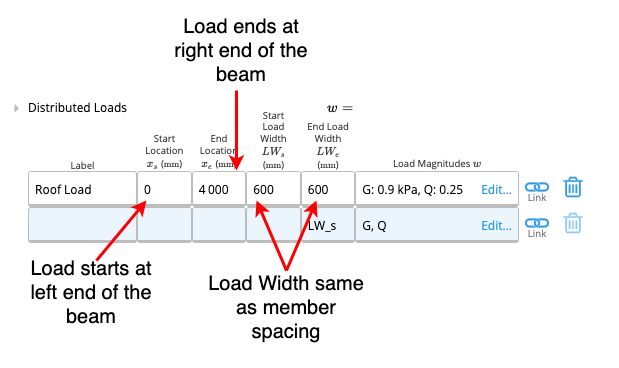
A. Start Location
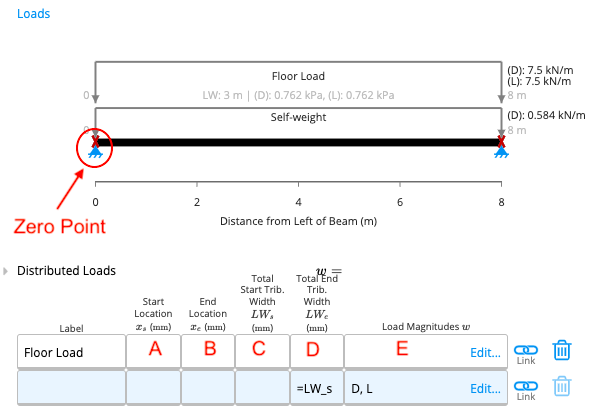
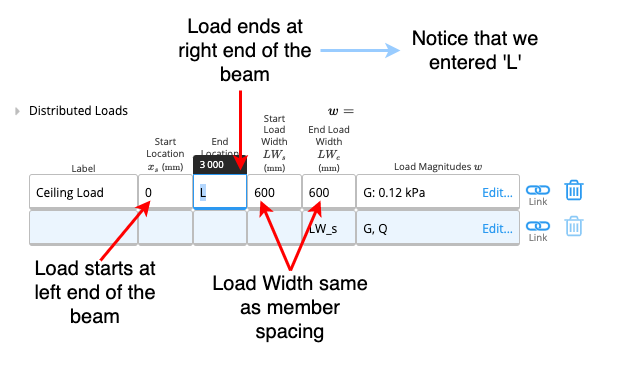
Start Location refers to the starting point of the load on the beam as measured from the left end of the beam (from the zero point). This parameter needs to be in millimetres, alternatively, conversion formulae can also be entered into the cell for convenience (similar to Excel).B. End Location
End Location refers to the point on the beam at which the distributed load ceases to act. This parameter is also measured from the left end (zero point) of the beam and needs to be in millimetres. If the end location is also the right end of the beam, you can input ‘L’ for convenience (see Example 1).C-D. Tributary Width / Load Width
Every structural element has an area from which it obtains its load. As with any other area, this can also be expressed as a product of length and width. The length of this area is usually either the length of the element itself or the length of the distributed load (B-A from the table). Tributary width is simply the width of this area.How to find Tributary Width?
To better illustrate this concept, consider a floor that is supported by members spaced ‘s’ mm apart.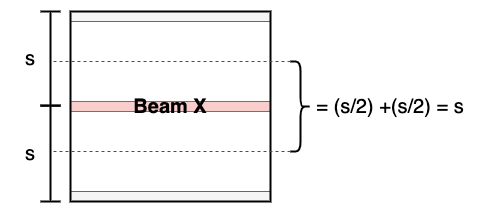 Consider beam X, where its tributary area has the same length as the beam and the tributary width is ‘s’. So for most cases, the tributary width is the same as member spacing. Notice that the tributary area is not always a rectangle and can instead take on a triangular shape. In such instances, the starting and ending tributary widths will be different.
Consider beam X, where its tributary area has the same length as the beam and the tributary width is ‘s’. So for most cases, the tributary width is the same as member spacing. Notice that the tributary area is not always a rectangle and can instead take on a triangular shape. In such instances, the starting and ending tributary widths will be different.
C. Total Start Tributary Width
Measured in millimetres, the total start tributary width refers to the width of the tributary area at the starting point of the distributed load.D. Total End Tributary Width
Measured in millimetres, the total end tributary width refers to the width of the tributary area at the ending point of the distributed load.E. Load Magnitudes
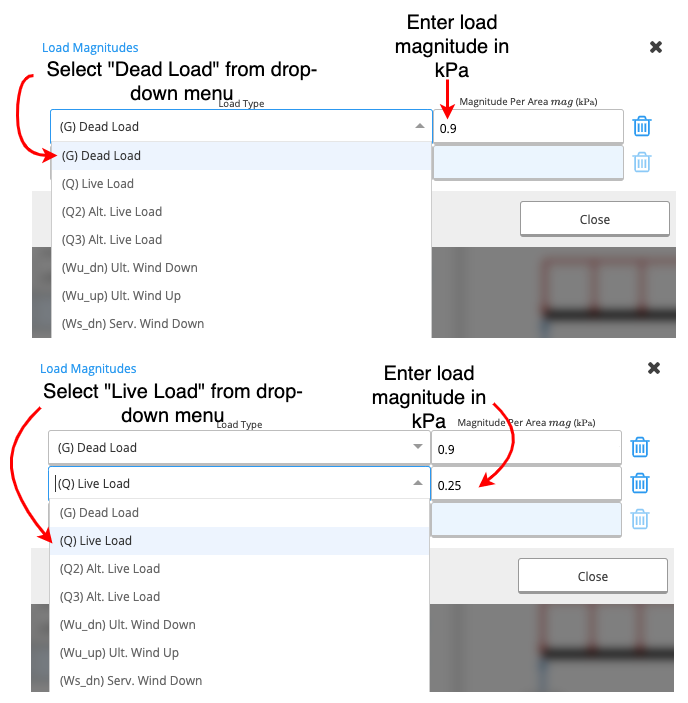
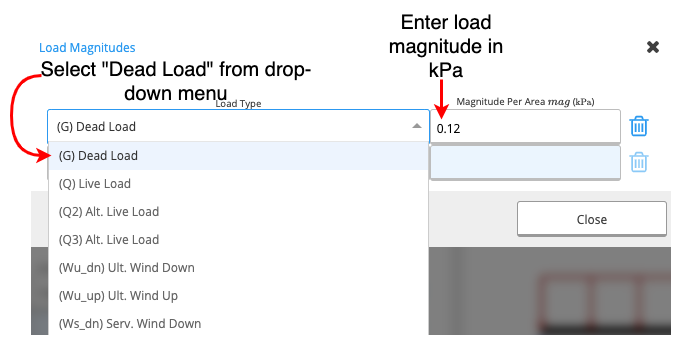
When you click on this cell, a new table will appear (see below).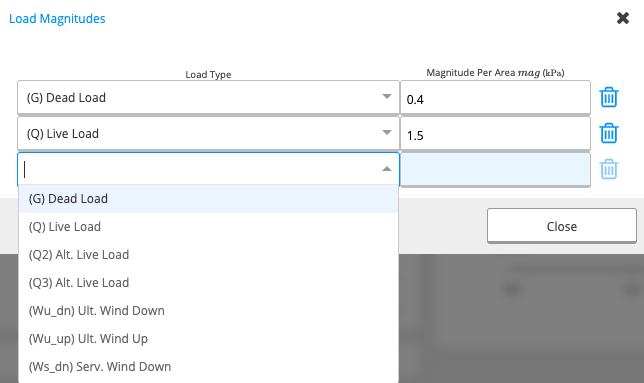
- First Column: A drop-down menu from which you can choose your load type.
- Second Column: You can input the magnitude of the load in kilopascals (kPa).
Example 1
Task
Input a live load of 1.5kPa on a floor joist with a member spacing of 450mm.Method
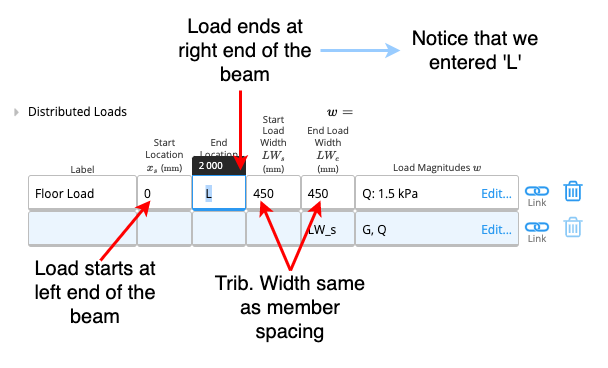
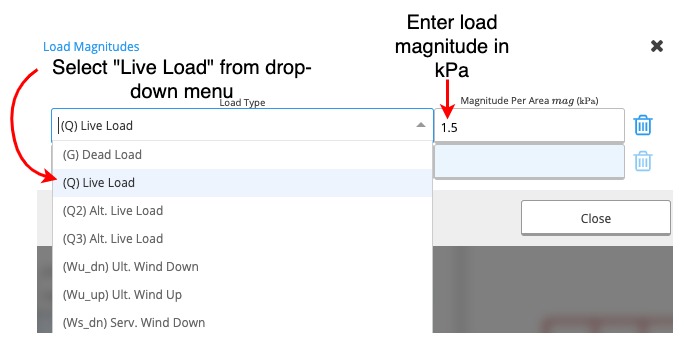
Example 2
Task
Input a dead load of 0.12kPa on a ceiling joist with a member spacing of 600mm.Method
Example 3
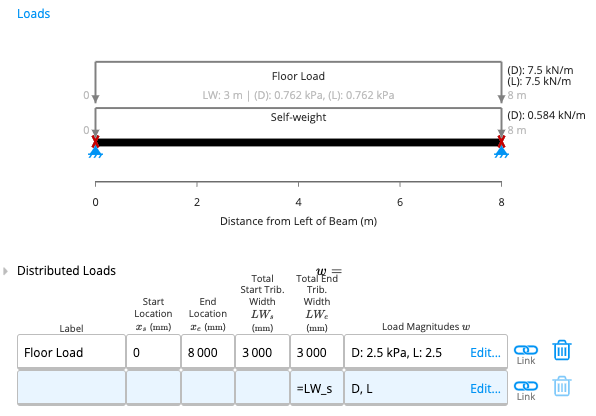
Task
Input a live load of 0.25kPa and a dead load of 0.9kPa on a rafter with 600mm member spacing.Method